Exercise challenge spirometry
Exercise challenge spirometry measures the amount of air that can be inhaled and exhaled following exertion, and can be used to assess a patient's exercise capacity. This technology is often used to provide additional information that may help with the diagnosis of patients with reduced exercise capacity and dyspnea (shortness of breath).
Contact
What is meant by exercise challenge spirometry?
Exercise challenge spirometry is a diagnostic procedure that can be used to assess how the heart, circulation, breathing and metabolism react to muscle activity, as well as making it possible to assess a patient's cardiopulmonary fitness.
When can exercise challenge spirometry help?
- Assessment of patients with dyspnea (shortness of breath) and reduced exercise capacity
- Evaluation of the severity of heart disease (e.g. heart failure) and the extent to which the condition impacts upon the patient's daily life
- Assessment to determine whether impairment relates to cardiac or pulmonary function
Treatment step-by-step
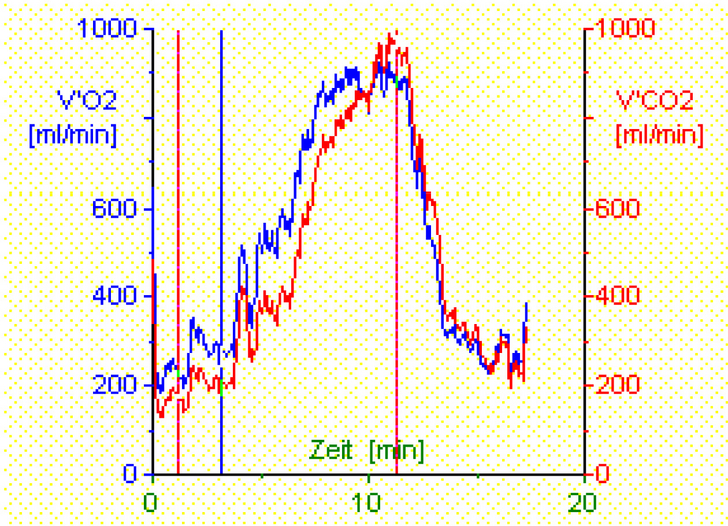
- Physical stress is induced by cycling on a stationary bike. Training intensity at the start of the test, as well as incremental increases in intensity, will depend on the individual patient. The patient will have to wear a face mask that closes tightly around the nose and mouth. This mask, which is fitted with a spirometer, measures both the flow and volume of air being breathed in and out. In addition to this, samples are taken and analyzed in order to obtain the oxygen and carbon dioxide content of the inhaled/exhaled air.
- A comparison with normal values can then be used to determine the patient's exercise capacity and cardiopulmonary function. In patients with severely impaired cardiopulmonary function, this test can also provide information on whether this impairment is caused primarily by heart disease, primarily by lung disease, or by a combination of the two.
VO2 max - CHF